Introduction
In the world of medicine, needles and syringes are essential tools that are used to administer medications, draw blood, and perform other medical procedures. These tools come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and it is important for healthcare workers to understand the differences between them and how to use them properly. In this article, we will provide a simple guide to medical needles and syringes.
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comThe Parts of a Needle
A needle consists of three parts: the hub, the shaft, and the bevel. The hub is the part of the needle that attaches to the syringe. The shaft is the long, thin part of the needle that penetrates the skin. The bevel is the slanted tip of the needle that allows it to pierce the skin more easily. Needles also come in different gauges, which refers to the thickness of the shaft. The higher the gauge, the thinner the needle.
The Parts of a Syringe
A syringe consists of three parts: the barrel, the plunger, and the needle. The barrel is the part of the syringe that holds the medication. The plunger is the part of the syringe that is used to push the medication out of the barrel and into the patient’s body. The needle is the part of the syringe that attaches to the hub of the needle. Syringes also come in different sizes, ranging from 1 mL to 60 mL.
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comThe Different Types of Needles
There are several different types of needles that are used for different types of medical procedures. Some of the most common types of needles include:
- Standard Hypodermic Needles: These needles are used for most medical procedures and come in a variety of sizes and gauges.
- Insulin Needles: These needles are used to administer insulin and are much thinner than standard hypodermic needles.
- Butterfly Needles: These needles have wings on the side that allow for easier insertion into the skin and are often used for drawing blood.
- Spinal Needles: These needles are used for spinal taps and other procedures that require access to the spinal canal.
- Epidural Needles: These needles are similar to spinal needles but are longer and are used for epidural anesthesia.
 Source: bing.com
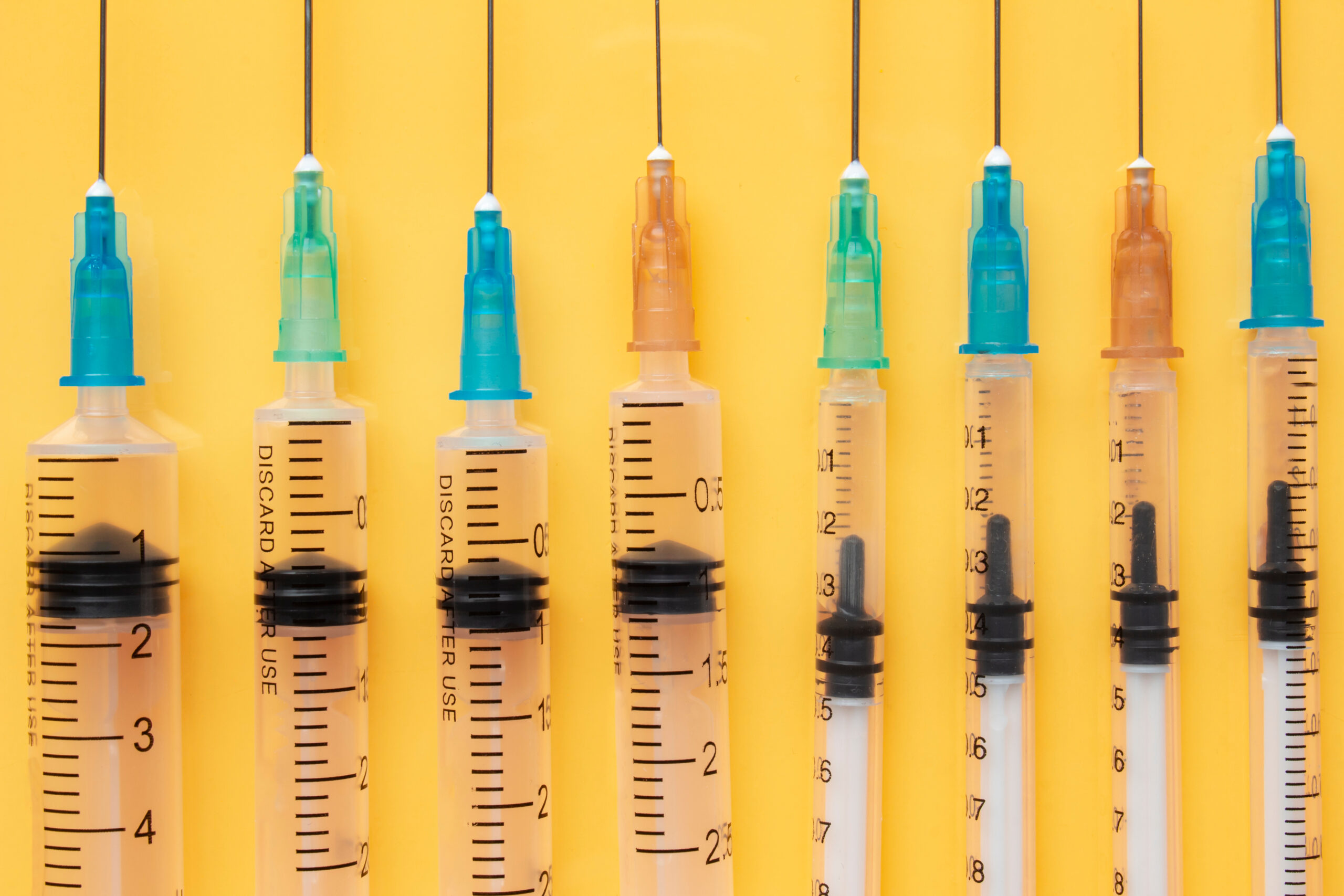
Source: bing.comThe Different Types of Syringes
Like needles, there are also several different types of syringes that are used for different types of medical procedures. Some of the most common types of syringes include:
- Standard Syringes: These syringes are used for most medical procedures and come in a variety of sizes.
- Insulin Syringes: These syringes are used to administer insulin and are much smaller than standard syringes.
- Tuberculin Syringes: These syringes are used for small injections, such as for tuberculosis tests.
- Pre-Filled Syringes: These syringes come pre-filled with medication and are often used for vaccines and other injectable medications.
- Oral Syringes: These syringes are used to administer medications orally, such as to infants or patients who cannot swallow pills.
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comHow to Use a Needle and Syringe
Using a needle and syringe properly is essential for patient safety. Here are the steps to follow:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Gather all necessary supplies, including the needle, syringe, medication, and alcohol swabs.
- Prepare the medication according to the instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
- Clean the injection site with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry.
- Remove the needle from its packaging and attach it to the syringe.
- Draw the medication into the syringe by pulling back on the plunger.
- Tap the syringe to remove any air bubbles.
- Insert the needle into the injection site at a 90-degree angle.
- Slowly push the plunger to inject the medication.
- Remove the needle from the injection site and discard it in a sharps container.
Conclusion
Needles and syringes are essential tools in the world of medicine, and it is important for healthcare workers to understand how to use them properly. By following the steps outlined in this article and understanding the different types of needles and syringes available, healthcare workers can ensure that patients receive the medications they need safely and effectively.