 Source: bing.com
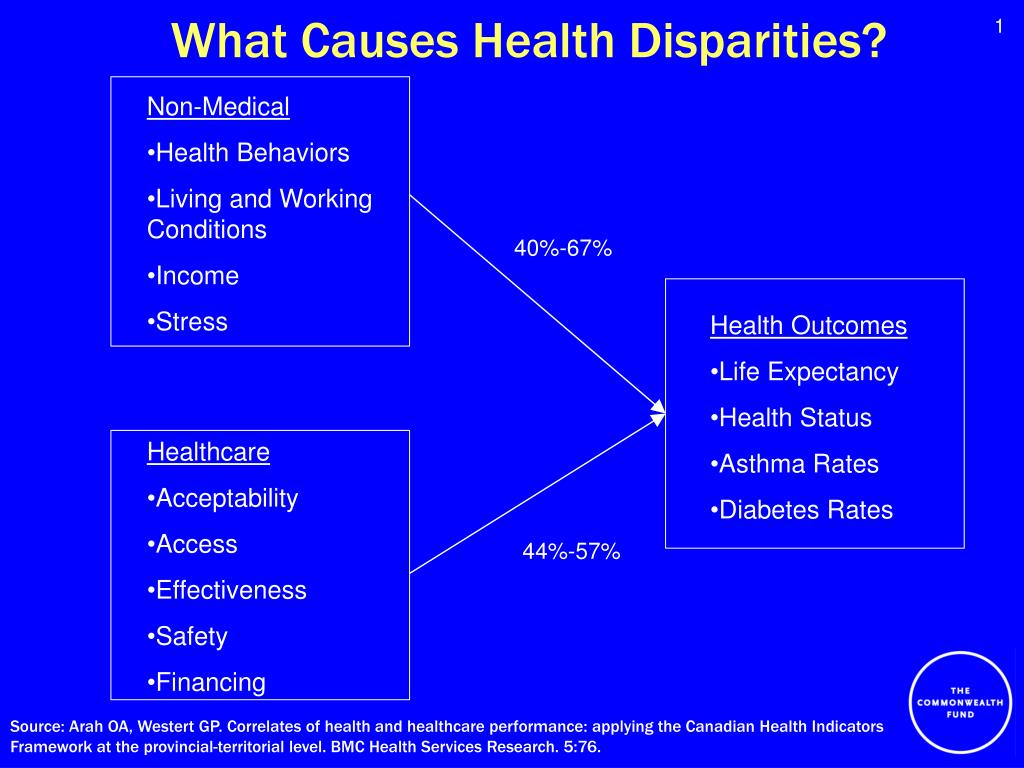
Source: bing.comHealth disparities refer to differences in the health outcomes of people in different populations or groups. These disparities can be seen in terms of differences in access to healthcare, quality of care, and health outcomes. Populations at risk are those groups of people who are more likely to experience health disparities. This article will discuss some of the populations at risk for health disparities and what can be done to address these disparities.
Low-Income Populations
 Source: bing.com
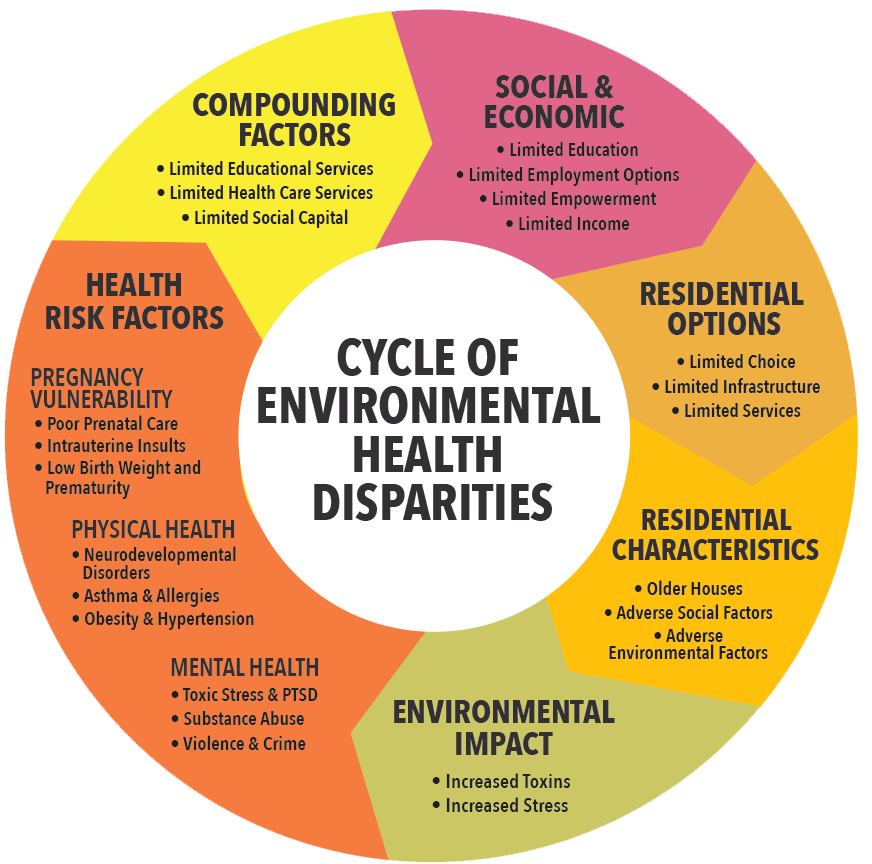
Source: bing.comLow-income populations are one of the most significant populations at risk for health disparities. These populations are more likely to have limited access to healthcare, healthy food options, and safe living environments. This lack of access can lead to chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity. Additionally, low-income populations often lack the resources to manage their health, including transportation to doctor appointments or medications. To address health disparities in low-income populations, it is important to increase access to healthcare, healthy food options, and safe living environments. Programs that provide education and resources for managing health can also be beneficial.
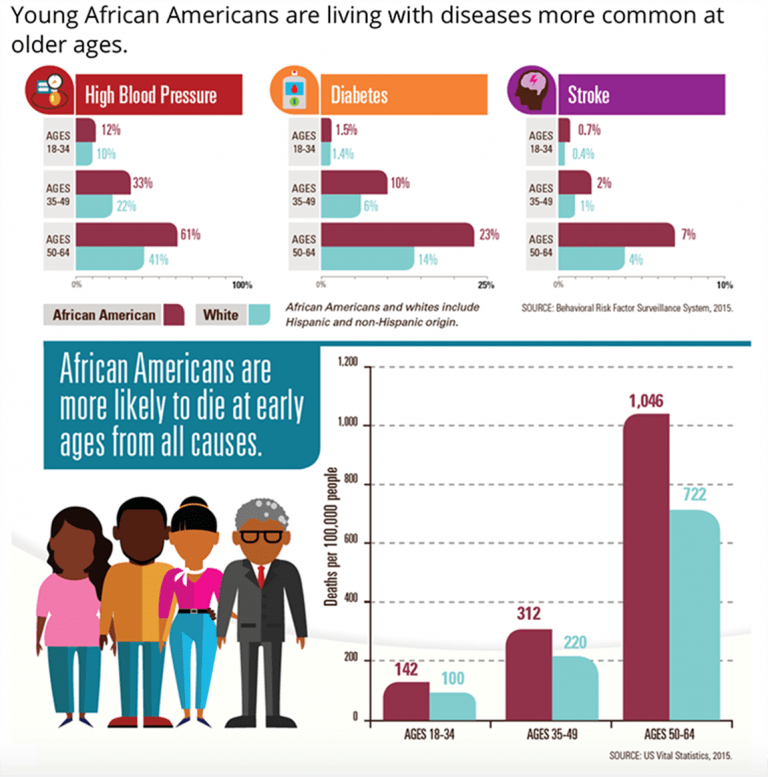
Racial and Ethnic Minorities
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comRacial and ethnic minorities are also populations at risk for health disparities. These populations often experience discrimination and racism, which can lead to stress and poor mental health outcomes. Additionally, racial and ethnic minorities are more likely to have limited access to healthcare and receive lower quality care when they do receive healthcare. This can lead to higher rates of chronic diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease. Addressing health disparities in racial and ethnic minorities requires increasing access to healthcare and providing culturally competent care. It is also important to address discrimination and racism to improve mental health outcomes.
Elderly Populations
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comElderly populations are another group at risk for health disparities. These populations often have multiple chronic conditions that require ongoing medical care. They may also have limited mobility or transportation, which can make accessing healthcare and other resources difficult. Additionally, elderly populations may experience social isolation, which can lead to poor mental health outcomes. To address health disparities in elderly populations, it is important to improve access to healthcare and resources. Programs that provide social support and opportunities for engagement can also be beneficial.
LGBTQ+ Populations
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comLGBTQ+ populations are another group at risk for health disparities. These populations often experience discrimination and stigma, which can lead to poor mental health outcomes. Additionally, LGBTQ+ populations may have limited access to healthcare that is culturally competent and inclusive of their identities. This can lead to higher rates of chronic diseases, such as HIV and depression. Addressing health disparities in LGBTQ+ populations requires increasing access to healthcare that is culturally competent and inclusive. It is also important to address discrimination and stigma to improve mental health outcomes.
Conclusion
Health disparities are a significant issue that affects many populations at risk. Addressing these disparities requires increasing access to healthcare, healthy food options, and safe living environments. It also requires providing culturally competent care and addressing discrimination and stigma. By taking steps to address health disparities in populations at risk, we can improve the health outcomes of all individuals and create a more equitable healthcare system.