Insulin syringe is a medical device used to inject insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. People with diabetes, particularly Type 1 diabetes, rely on insulin injections to manage their condition. Insulin syringes are the most common method of delivering insulin, and they come in different sizes and needle gauges.
Types of Insulin Syringes
 Source: bing.com
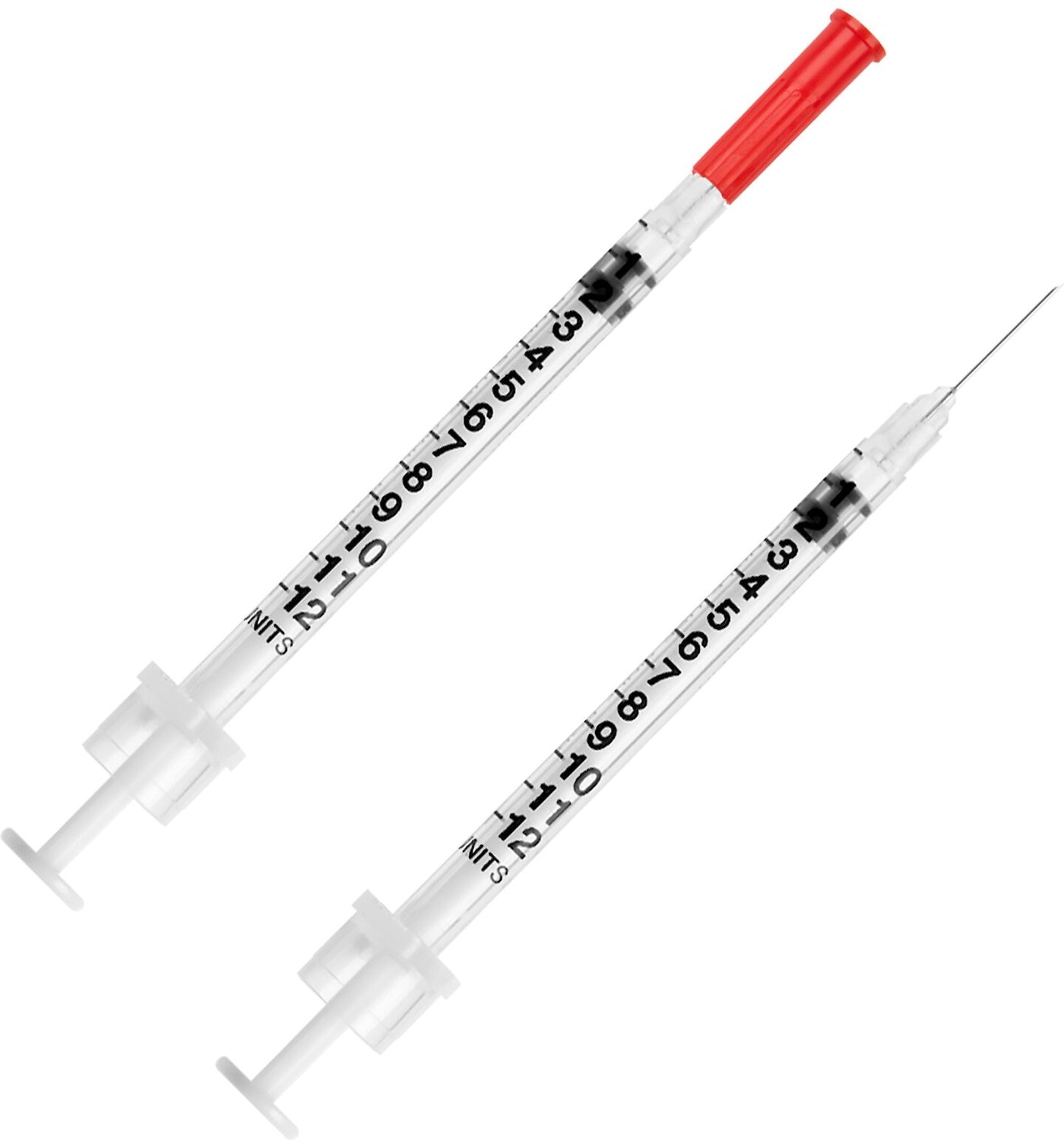
Source: bing.comThere are two main types of insulin syringes: U-100 and U-40. U-100 syringes are the most common ones, and they are designed to hold insulin that has a concentration of 100 units per milliliter. U-40 syringes, on the other hand, hold insulin with a concentration of 40 units per milliliter. Diabetic patients should always use the syringes that match the insulin concentration they are using to ensure the right dosage.
Parts of Insulin Syringes
 Source: bing.com
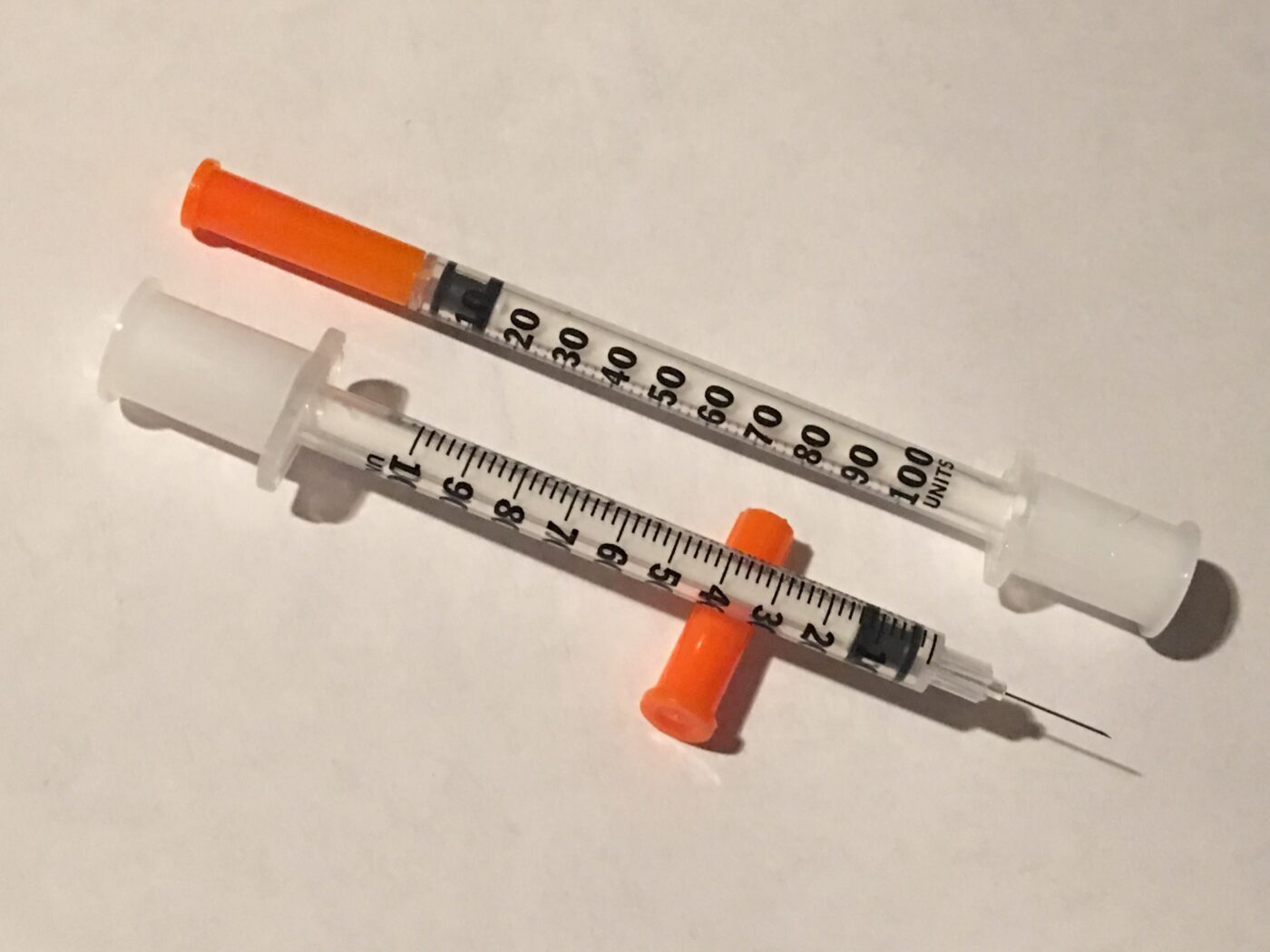
Source: bing.comInsulin syringes consist of four main parts: the barrel, plunger, needle, and cap. The barrel is the cylindrical part that holds the insulin. The plunger is the rod-like part used to push the insulin out of the syringe. The needle is the thin, sharp metal tip that penetrates the skin. The cap covers the needle and protects it from damage.
Syringe Size and Needle Gauge
Syringe size refers to the volume of insulin the syringe can hold, and it is measured in milliliters (ml) or cubic centimeters (cc). The most common syringe sizes are 1ml, 0.5ml, and 0.3ml. Needle gauge, on the other hand, refers to the thickness of the needle. The smaller the gauge number, the thicker the needle. Most insulin syringes come with a needle gauge of 28 to 31. The right syringe size and needle gauge depend on the patient's insulin dose and skin thickness.
How to Use Insulin Syringes
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comUsing insulin syringes requires proper technique to ensure accurate dosing and minimize pain and discomfort. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use insulin syringes:
1. Wash your hands with soap and water to prevent infection.
2. Assemble the insulin syringe by attaching the needle to the barrel.
3. Draw the required insulin dose into the syringe by pulling the plunger back until the desired amount is reached.
4. Tap the syringe gently to remove any air bubbles. Push the plunger slightly to expel the air, making sure the needle tip is pointing upward.
5. Choose an injection site and clean it with an alcohol swab. The most common injection sites are the abdomen, thighs, and buttocks.
6. Hold the syringe like a pencil with your dominant hand and use the other hand to pinch the skin at the injection site.
7. Insert the needle into the skin at a 90-degree angle for most adults, or a 45-degree angle for children and thin adults. Push the plunger slowly to inject the insulin.
8. Remove the needle from the skin and discard the syringe in a sharps container.
Benefits of Insulin Syringes
 Source: bing.com
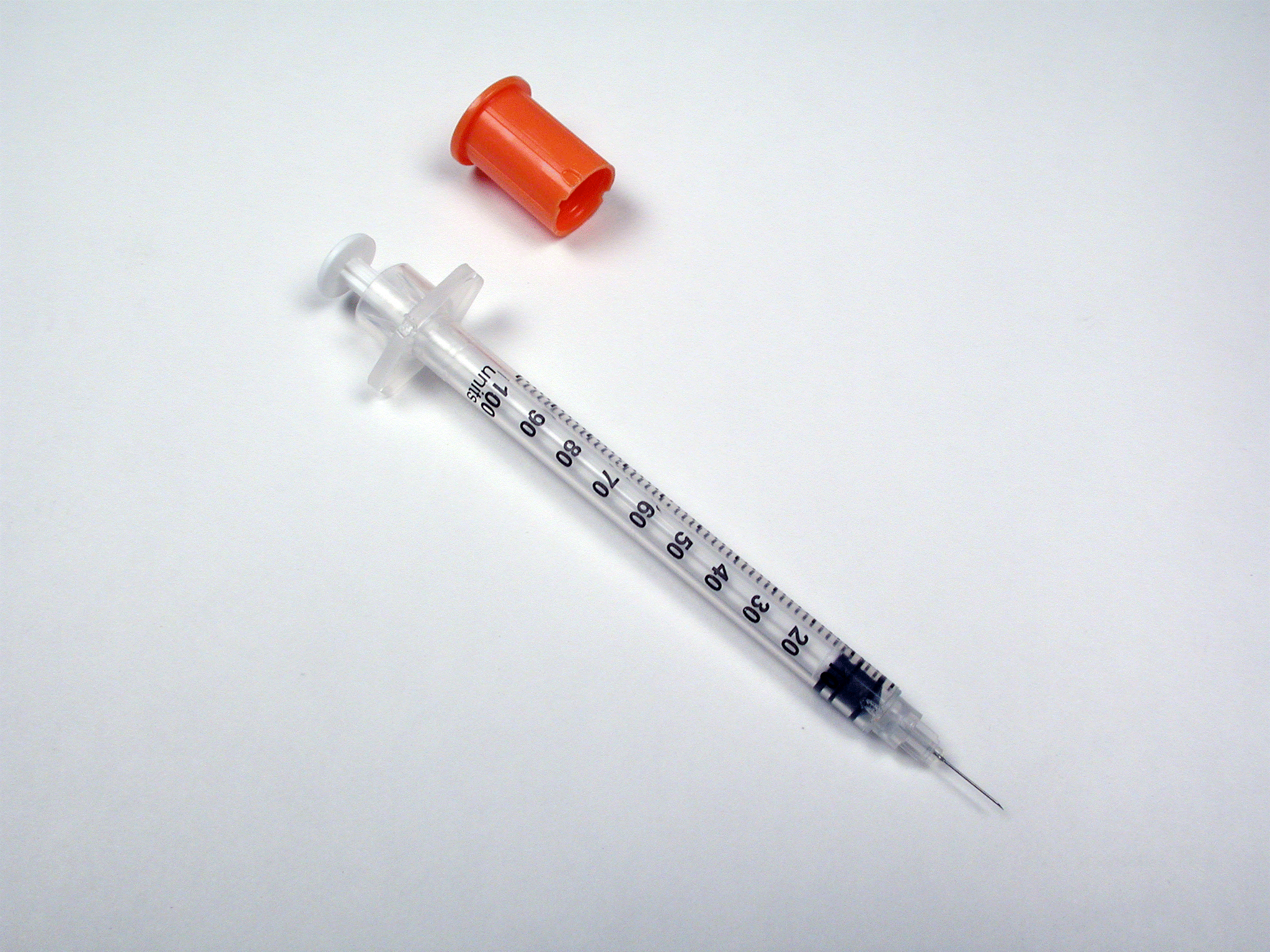
Source: bing.comInsulin syringes offer several benefits for diabetic patients, including:
1. Accurate dosing: Insulin syringes allow for precise measurement of insulin doses, ensuring patients get the right amount of insulin they need to manage their condition.
2. Convenience: Insulin syringes are portable and easy to use, making it easier for patients to administer insulin injections wherever they are.
3. Cost-effective: Insulin syringes are relatively inexpensive compared to other insulin delivery methods, such as insulin pens and pumps, making them a cost-effective option for patients.
Precautions When Using Insulin Syringes
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comWhen using insulin syringes, diabetic patients should take the following precautions to ensure their safety:
1. Use a new needle and syringe for each injection to prevent contamination and infection.
2. Do not share syringes with other people to avoid the risk of transmitting blood-borne diseases, such as HIV and hepatitis.
3. Follow proper injection technique to minimize pain and discomfort and avoid injury.
4. Store the insulin syringes at room temperature and avoid exposure to extreme heat or cold to prevent degradation of the insulin.
Conclusion
Insulin syringes are an essential tool for diabetic patients who require insulin injections to manage their condition. They come in different sizes and needle gauges, and they offer several benefits, such as accurate dosing, convenience, and cost-effectiveness. However, it is crucial for diabetic patients to follow proper injection technique and take necessary precautions when using insulin syringes to ensure their safety and well-being.