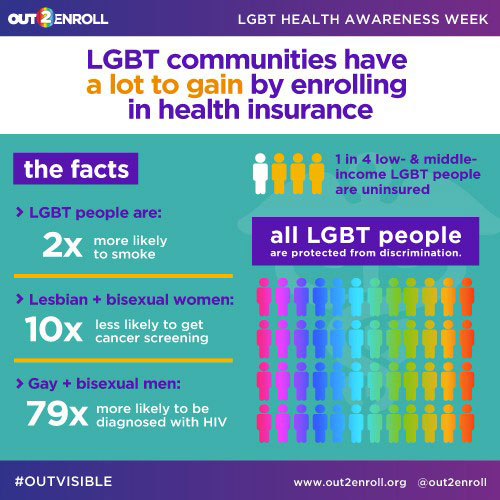
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comLesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, and Queer (LGBTQ) youth have unique health considerations and face many challenges that may impact their physical and mental well-being. Discrimination, stigma, and lack of acceptance from their communities, families, and peers can lead to negative health outcomes such as depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts.
Understanding LGBTQ Terminology
Before discussing health considerations for LGBTQ youth, it's important to understand the terminology used to describe different sexual orientations and gender identities. Sexual orientation refers to an individual's emotional and sexual attraction to others. LGBTQ individuals may identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, pansexual, asexual, or queer. Gender identity refers to an individual's sense of self as male, female, or something else. Transgender individuals may identify as male, female, non-binary, or genderqueer.
Mental Health Concerns
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comLGBTQ youth are at increased risk for poor mental health outcomes, such as depression, anxiety, and suicidal ideation. They may experience bullying, harassment, and social isolation, which can lead to feelings of low self-worth. It's important for parents, educators, and healthcare professionals to be aware of the unique challenges faced by LGBTQ youth and to provide support and resources to help them cope with these stressors.
Sexual Health Concerns
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comLGBTQ youth may face barriers to accessing healthcare services related to sexual health, such as HIV testing and contraception. They may also be at increased risk for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancy. It's important for healthcare providers to create welcoming and non-judgmental environments for LGBTQ youth seeking sexual health services.
Substance Abuse
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comLGBTQ youth may be at increased risk for substance abuse due to discrimination, rejection, and social isolation. They may use drugs and alcohol as a coping mechanism to deal with the stressors of being part of a stigmatized group. It's important for parents and healthcare providers to monitor substance use in LGBTQ youth and provide support and resources for substance abuse treatment.
Physical Health Concerns
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comLGBTQ youth may face disparities in healthcare access and quality, which can lead to negative health outcomes. They may be less likely to have health insurance or to seek preventative care services. They may also face discrimination and bias from healthcare providers, which can lead to inadequate care. It's important for healthcare providers to be aware of these disparities and to work towards providing equitable healthcare for LGBTQ youth.
Family Acceptance
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comFamily acceptance is a key factor in the health and well-being of LGBTQ youth. Youth who are rejected by their families are more likely to experience depression, anxiety, and suicidal thoughts. It's important for parents and caregivers to provide support and acceptance for their LGBTQ children, and to seek out resources and support groups if needed.
Conclusion
LGBTQ youth face unique health challenges related to their sexual orientation and gender identity. It's important for healthcare providers, parents, and educators to be aware of these challenges and to provide resources and support to help LGBTQ youth thrive. By creating welcoming and supportive environments, we can help ensure that all youth, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity, have the opportunity to live healthy and fulfilling lives.