 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comIntroduction
G-Tube feeding, also known as gastrostomy tube feeding, is a method of providing nutrition to individuals who are unable to swallow food or fluids. This can be due to a variety of reasons such as a medical condition, injury, or surgery. In this article, we will discuss some helpful G-Tube feeding tips for caregivers and patients.
Preparing for Feeding
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comBefore starting the feeding process, it is important to prepare the equipment and supplies needed. This includes a feeding bag, syringe, feeding formula, and water. Wash your hands thoroughly and make sure the feeding formula is at room temperature before administering it through the G-Tube.
Positioning
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comPositioning is important during G-Tube feeding. The patient should be in an upright position during feeding and remain in this position for at least 30 minutes after feeding to prevent reflux or aspiration. If the patient is unable to sit up, a reclined position can be used.
Feeding Schedule
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comA feeding schedule should be established based on the patient's needs and medical condition. It is important to follow the prescribed feeding schedule and not to skip or delay feedings. If the patient experiences any discomfort or pain during feeding, consult with a healthcare professional.
Cleaning and Maintenance
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comThe G-Tube site should be cleaned daily with soap and water and inspected for any signs of infection or irritation. The feeding equipment should also be cleaned after each use and replaced every few months to prevent wear and tear. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions for cleaning and maintenance.
Monitoring
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comIt is important to monitor the patient's weight, urine output, and bowel movements regularly to ensure proper nutrition and hydration. Any changes in these factors should be reported to a healthcare professional.
Fluid Intake
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comThe patient should be encouraged to drink fluids in addition to G-Tube feedings to maintain proper hydration. Water or other non-caffeinated, non-carbonated beverages are recommended.
Formula Selection
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comThe formula used for G-Tube feeding should be selected based on the patient's medical condition and nutritional needs. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate formula and feeding regimen.
Syringe Feeding
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comSyringe feeding can be used for patients who are unable to tolerate continuous feedings or large volumes of formula at once. This method involves slowly administering small amounts of formula through a syringe. Consult with a healthcare professional for proper technique and dosing.
Bolus Feeding
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comBolus feeding involves administering a large volume of formula at once, typically 250-500 mL, over a short period of time. This method should only be used for patients who can tolerate large volumes of formula and have a properly functioning G-Tube. Consult with a healthcare professional for proper technique and dosing.
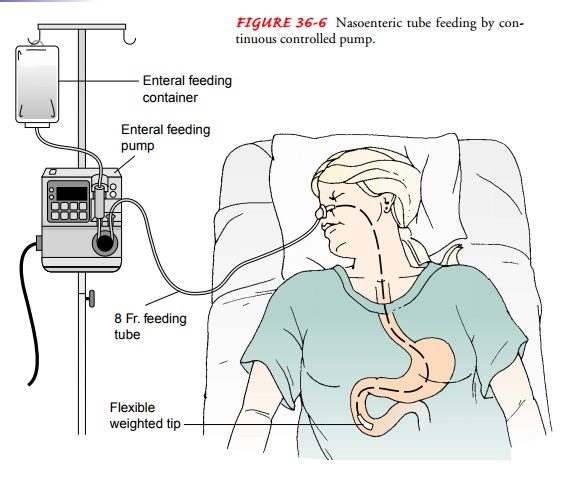
Pump Feeding
Pump feeding involves administering a continuous flow of formula through a pump. This method is often used for patients who require slow, continuous feedings. Consult with a healthcare professional for proper pump settings and dosing.
Medication Administration
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comMedications can be administered through a G-Tube by crushing them and mixing them with water or a small amount of formula. Consult with a healthcare professional before administering any medications through a G-Tube.
Traveling with a G-Tube
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comWhen traveling with a patient who has a G-Tube, it is important to bring all necessary supplies and equipment. This includes extra feeding formula, syringes, and a backup G-Tube. Consult with a healthcare professional for specific travel recommendations.
Signs of Complications
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comIt is important to be aware of the signs of complications from G-Tube feeding. These include fever, redness or swelling at the G-Tube site, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. If any of these symptoms occur, seek medical attention immediately.
Training and Education
 Source: bing.com
Source: bing.comCaregivers should receive proper training and education on G-Tube feeding before administering it to a patient. This includes proper technique, cleaning and maintenance, and recognizing signs of complications.
Conclusion
G-Tube feeding can be a challenging but necessary aspect of caring for a patient who is unable to swallow food or fluids. By following these helpful tips, caregivers can ensure the patient receives proper nutrition and hydration while minimizing the risk of complications.